What is ESR?
ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate) is a simple blood test. It measures how quickly red blood cells settle at the bottom of a test tube. Usually, red blood cells settle slowly. However, when there is inflammation in the body, they may settle faster. Because of this, doctors use the ESR blood test to check for signs of inflammation or certain diseases. The test does not show the exact cause, but it helps guide further testing.
Why is the ESR Test Done?
Doctors order the ESR test for several reasons. Often, it helps them look for inflammation in the body. Sometimes, it is used to monitor ongoing health problems. For example, it can help track conditions like arthritis or infections. In addition, the ESR test may help find out if a treatment is working. Here are some common reasons for the test:
How is the ESR Test Performed?
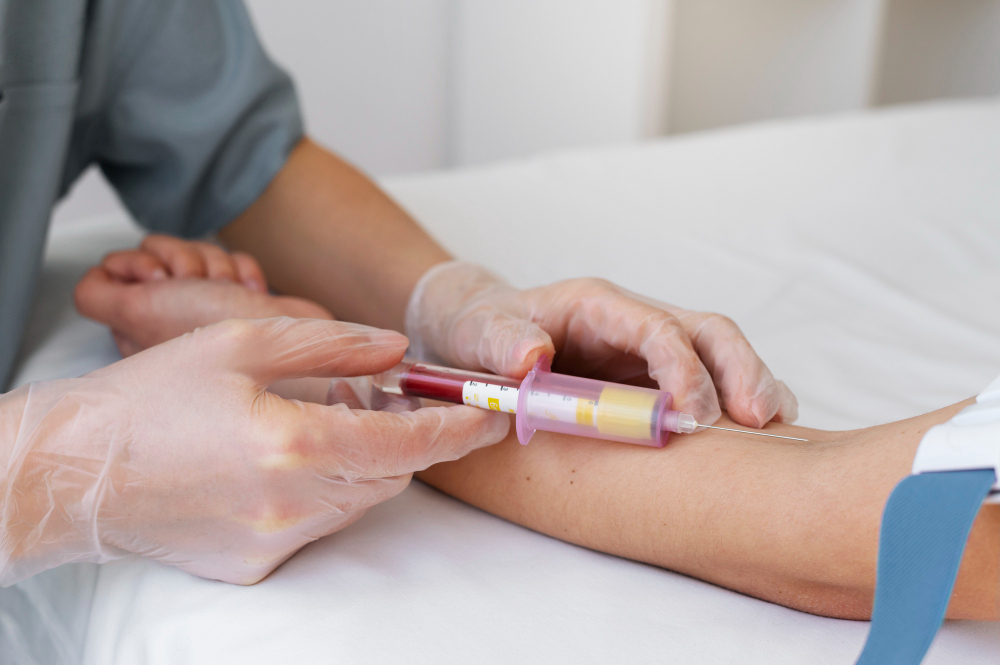
The ESR blood test is quick and simple. First, a healthcare worker takes a small blood sample from your arm. Next, the sample goes to a lab. There, the lab measures how fast the red blood cells fall in a tube over one hour. The result is given in millimeters per hour (mm/hr). You do not need to fast or prepare in any special way for this test. Most people feel only a small pinch during the blood draw.
Normal ESR Levels
Normal ESR levels can vary by age and gender. However, most healthy adults have an ESR between 0 and 20 mm/hr. Children often have lower levels. Women and older adults may have slightly higher normal values. Here are some general guidelines:
Still, normal ranges may differ between labs. Therefore, always check with your doctor about your specific results.
Causes of High or Low ESR
Sometimes, ESR results are higher or lower than normal. This can happen for many reasons. High ESR causes often include:
On the other hand, low ESR is less common. It may be seen with:
However, many things can affect ESR. For example, pregnancy, age, and some medicines may change your results.
What Do ESR Results Mean?
It is important to remember that ESR is a general test. A high or low ESR does not point to one specific disease. Instead, it shows that something may be wrong. Because of this, doctors use ESR results along with other tests and your symptoms. Sometimes, a high ESR is not a cause for worry. Other times, it may signal a health problem that needs more attention. Always talk to your doctor about what your ESR test meaning is for you.
When to Consult a Doctor
If your ESR levels are not normal, do not panic. Many things can cause changes in ESR. However, you should consult a doctor if:
Early advice can help find the cause and guide treatment. Therefore, do not ignore abnormal results.
Frequently Asked Questions about ESR
If you have questions about your ESR results, consult a healthcare professional at Rapid Diagnostics for personalized advice.